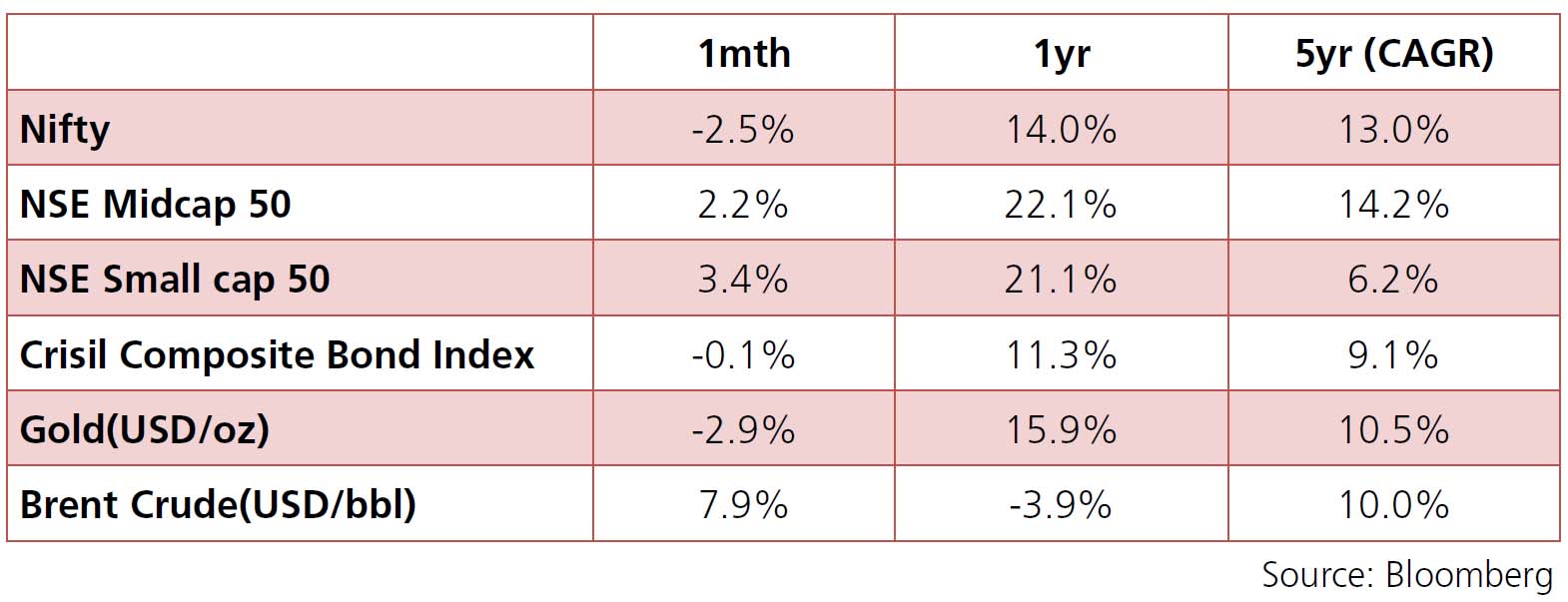
Month Gone By – Markets (period ended January 29, 2021)
Equity indices globally and domestically saw some moderation towards the end of January after
witnesssing dizzying heights during the mid of January. While in the USA, S&P 500 recorded lifetime
highest close on January 25th at 3855 bolstered by news of stimulus amounting to USD 2tn,
it was quick to close at 3714 on January 29th as investors trimmed their posistions due to a slew
of data on earnings for the quarter, GDP for Q4 and FOMC outcomes were expected.
In line with global equities, Indian equities also saw a sharp rally in January, with Nifty recording ever highest close of 14644 on Janaury 20th but was quick to moderate to 13634 on January 29th as traders and investors turned cautious and moderated their holdings to account for the Union Budget due to be presented on February 1st. The initial rally was bolstered by FPI buying which amounted to USD 3bn, while caution at the outset of budget got better of the rally and recorded a correction by the month end. Sector-wise, CNX Auto was the best performer of the lot recording a rally of 6.7%, while CNX Pharma remained a laggard recording a fall of 5.8%, followed by CNX Energy at 4.5%. Following the expansionary note of Union Budget 2021 presented on February 1st, which budgeted an increase of ~35% in capital expenditure at Rs 5.54Tn while allaying any fears of increase in taxation, Nifty closed the day at 14326 (+5% d-o-d).
INR gained much lost ground owing to strong dollar inflows and weakening DXY and ended the month at 72.88/USD in January
In line with global equities, Indian equities also saw a sharp rally in January, with Nifty recording ever highest close of 14644 on Janaury 20th but was quick to moderate to 13634 on January 29th as traders and investors turned cautious and moderated their holdings to account for the Union Budget due to be presented on February 1st. The initial rally was bolstered by FPI buying which amounted to USD 3bn, while caution at the outset of budget got better of the rally and recorded a correction by the month end. Sector-wise, CNX Auto was the best performer of the lot recording a rally of 6.7%, while CNX Pharma remained a laggard recording a fall of 5.8%, followed by CNX Energy at 4.5%. Following the expansionary note of Union Budget 2021 presented on February 1st, which budgeted an increase of ~35% in capital expenditure at Rs 5.54Tn while allaying any fears of increase in taxation, Nifty closed the day at 14326 (+5% d-o-d).

INR gained much lost ground owing to strong dollar inflows and weakening DXY and ended the month at 72.88/USD in January
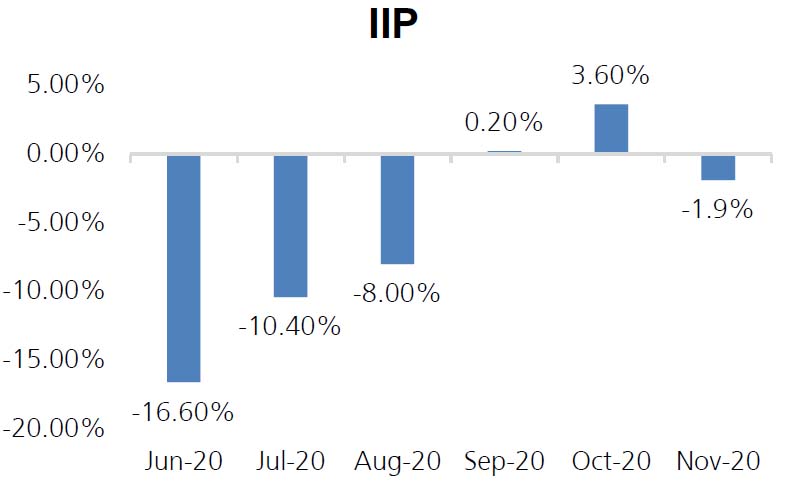
IIP: Index for Industrial Production for November saw a contraction of 1.90% YoY (vs. +3.60%% in
October). Consumer durables which recorded a rise of 4.97% m-o-m in October, saw the sharpest
fall of 13.29% m-o-m followed by Capital Goods which saw a fall of 7.65% m-o-m.
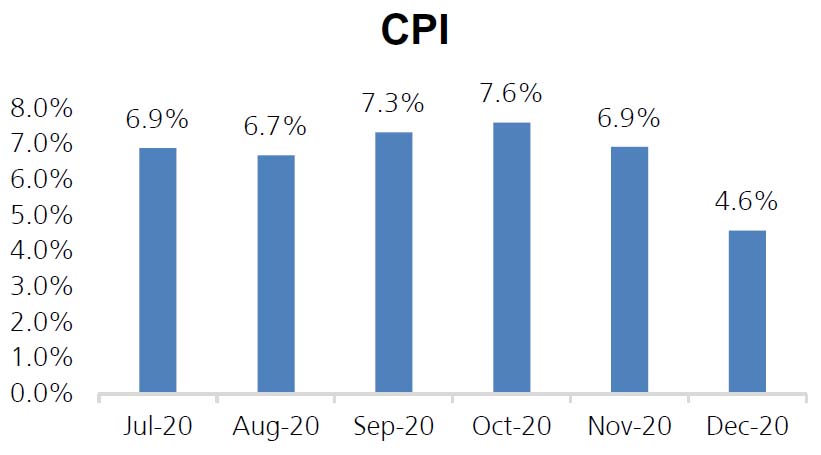
CPI: Headline CPI saw a sharp decline at 4.59% compared to 6.9% for the month of November and 7.6% in October. The easing was led by high base effect ( December 2019 @ 7.35%) and moderation in food inflation (December @ 3.4% vs 9.4% in November).
Trade Deficit: India recorded a trade deficit of USD 14.75Bn in January against a trade deficit recorded at USD 15.5Bn recorded in December. Cumulatively, exports during April-January 2020-21 contracted by 13.66% to USD 228.04Bn as against USD 264.13Bn for the corresponding period last fiscal. Imports are similarly down by 26% at USD 300Bn for April-January 2021 versus the corresponding period of last fiscal. Steepest rise in imports has been recorded by Gold this fiscal at 155%.
Fiscal Deficit: As of December end, India’s fiscal deficit widened to over Rs11.6Tn, ~62% of the revised annual target as the fall in revenue collections and divestments at Rs 160Bn (vs budgeted Rs 2.1Tn) refused to keep pace with the expenditure which carried on at similar levels as last year.
CPI: Headline CPI saw a sharp decline at 4.59% compared to 6.9% for the month of November and 7.6% in October. The easing was led by high base effect ( December 2019 @ 7.35%) and moderation in food inflation (December @ 3.4% vs 9.4% in November).
Trade Deficit: India recorded a trade deficit of USD 14.75Bn in January against a trade deficit recorded at USD 15.5Bn recorded in December. Cumulatively, exports during April-January 2020-21 contracted by 13.66% to USD 228.04Bn as against USD 264.13Bn for the corresponding period last fiscal. Imports are similarly down by 26% at USD 300Bn for April-January 2021 versus the corresponding period of last fiscal. Steepest rise in imports has been recorded by Gold this fiscal at 155%.
Fiscal Deficit: As of December end, India’s fiscal deficit widened to over Rs11.6Tn, ~62% of the revised annual target as the fall in revenue collections and divestments at Rs 160Bn (vs budgeted Rs 2.1Tn) refused to keep pace with the expenditure which carried on at similar levels as last year.
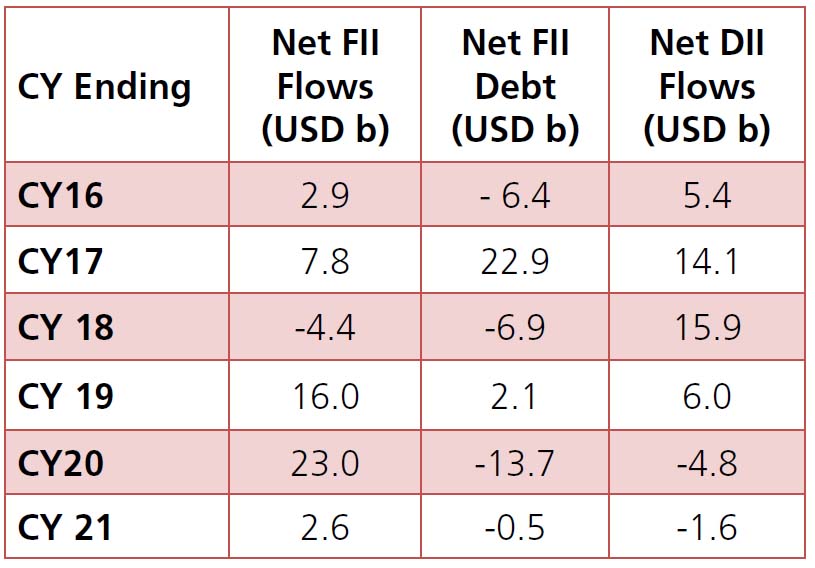
~USD2.7Bn in Dec) notable ones being SAIL’s
OFS (~USD185Mn), Indian Railway Finance
Corporation (~USD608Mn), Indigo Paints
(~USD159Mn) and Home First IPO (~USD158Mn)
FIIs were net buyers of ~USD1.8Bn (vs net inflow
of ~USD7.3Bn in Dec) in January but momentum
faded as they sold ~USD1.6Bn worth in the
last week. DIIs were net sellers of ~USD1.6Bn
during the month, majorly from Domestic MFs
(-USD2.1Bn).

